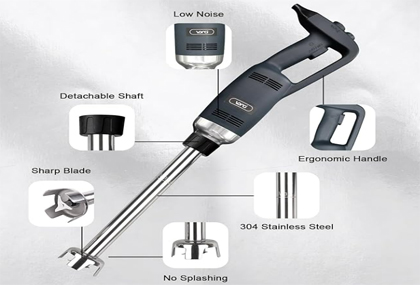
Application and Design Analysis of Internal Fixing Screws in Mixing Equipment
Mar 13,2025
398
In the field of mechanical transmission, the structural stability and safety of mixing equipment are always the core of the design. Among them, the fixed screw is used as the basic connector, and its design form and installation position directly affect the performance of the equipment. This paper will analyze whether the mixing equipment adopts internal fixed screws from a technical point of view, and discuss its engineering value.
First, the technical definition of internal fixation screws
Internal Fixation Screw refers to a fixed component hidden inside the device through a special structural design. Common forms include:
Countersunk Screw: The head is fully embedded in the mounting plane
Socket Head Cap Screw: Operated with a hex wrench
Insert nut: a metal nut embedded in the material
Its core advantages are:
Eliminate external protruding structures to avoid mechanical interference
Improve the surface flatness of the equipment for easy cleaning and maintenance
Enhance the overall structural strength and disperse stress concentration
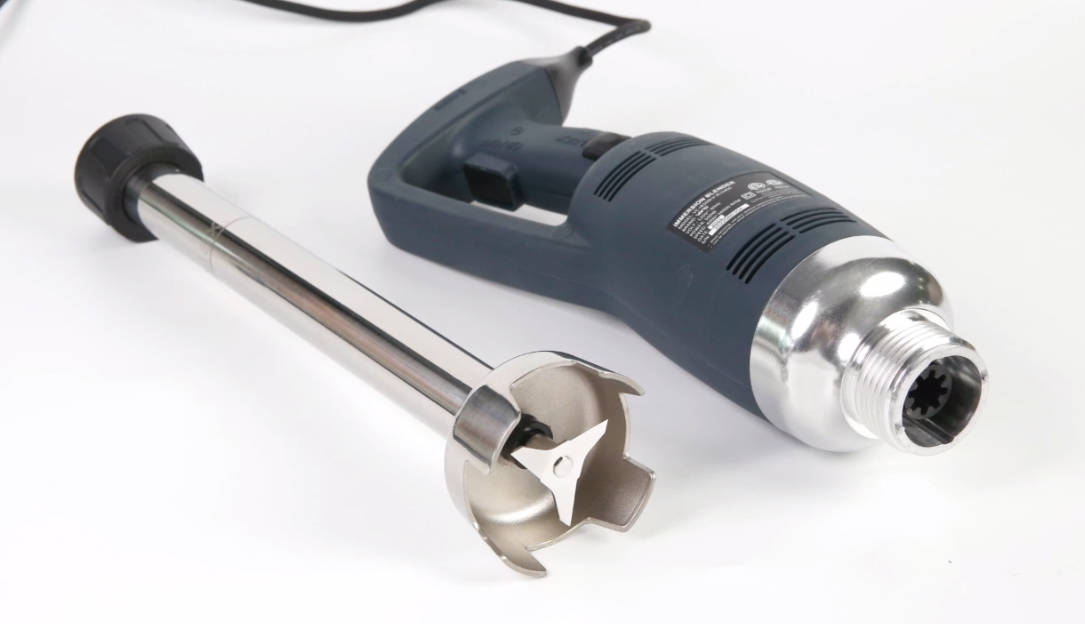

Second, the typical fixed scene of mixing equipment
In the mixing system, screw fixation is mainly used in three key parts:
Transmission system connection
Coupling fixation of motor shaft and stirring shaft
Assembly connection between gearbox and frame
Positioning and Installation of Bearing Housing and Support Arm
Stirring assembly fixed
The blade is fixed with the keyway of the stirring shaft
Axial Positioning of Multi-layer Stirring Propeller
The connection between the auxiliary scraper and the inner wall of the container
Sealed structure strengthening
The sealing flange of the end cover and the cylinder body is fixed
Installation of observation windows and pressure sensors
Quick opening and closing design of access port
III. Engineering application advantages of internal fixing screws
mechanical properties optimization
Made of high-strength alloy steel (e.g. 35CrMoA)
Thread accuracy above ISO 6
The preload is controlled within 70% of the material's yield strength
Environmental Adaptive Design
Surface treatment: nickel plating/chrome plating/dacromet process
Anti-loose structure: spring washer/anaerobic glue/self-locking nut
Sealing design: O-ring with threaded sealant
Maintenance convenience improvement
Reserved maintenance space (≥ 2 times the operating radius of the wrench)
Adopt anti-corrosion coating (salt spray test ≥ 1000 hours)
Key screw setting torque marking (for regular inspection)
IV. Comparison of alternative fixed solutions
Fixed method, applicable scenarios, advantages and disadvantages analysis
Welded connection, permanent structure, high strength but impossible to remove
Expansion sleeve connection, high torque transmission, easy installation but high cost
Snap-on connection, quick disassembly and assembly of components, poor sealing and limited load-bearing capacity
Hydraulic nuts, large equipment installation, require special tools but are highly accurate
V. Industry standards and safety regulations
ISO 6150-1:2021: Safety requirements for mixing equipment
Specify the minimum breaking strength of the fixing screws for rotating parts
Clarify the anti-loosening torque standard of exposed screws
ASME B18.3: Hex Screw Dimensions Standard
Define the load-bearing capacity parameters of screws of different specifications
Specify the corrosion resistance grade of the surface treatment
GB 19871-2005: Safety requirements for mixers
Requires periodic non-destructive testing of key fixing screws (e.g. ultrasonic flaw detection)
VI. Future development trends
Intelligent fastening technology
Smart screws with integrated torque sensor
Wireless monitoring systems (e.g. LoRa/NB-IoT)
Application of new materials
Carbon fiber reinforced composite screws
shape memory alloy fasteners
Additive Manufacturing Innovation
Integrated embedded fixed structure
3D printed profiled thread design
In modern mixing equipment, internal fixing screws have evolved from simple connectors to systematic solutions. By optimizing material selection, structural design and installation processes, it can not only ensure the stability of equipment operation, but also meet the needs of the new era such as clean production and intelligent maintenance. In the future, with the development of intelligent manufacturing technology, the functional boundaries of fixing screws will be further expanded, becoming a key node connecting mechanical entities and digital twins.